Strengthening STEM
America’s STEM Divide—A National Crisis
Historically, the United States has been regarded as a preeminent force in science and technology; however, today’s current graduates are not meeting the nation’s STEM workforce needs. The gap in American students completing science, technology, engineering and math degrees has created a significant “divide” that must be overcome in order to meet economic projections for future STEM professionals.
FAST FACTS—Science, Technology, Engineering and Math
*information courtesy of National Math & Science Initiative website and the 2012 PCAST Report, ENGAGE TO EXCEL: Producing One Million Additional College Graduates with Degrees in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics
- 38% of students who start college with a STEM major do not graduate with one.
- 69% of high school graduates are not prepared for college-level science.
- By 2022, the United States will need approximately 1 million more STEM professionals.
- To meet demand, the number of U.S. students earning undergraduate STEM degrees must increase by 34% annually over current rates.
Retaining STEM Majors is a Primary Concern
Retaining more students in science, technology, engineering and math majors is the lowest cost, fastest policy option to providing the STEM professionals that the nation needs for economic and societal well being. PCAST’s report indicated that many of the students who abandon STEM majors perform well in their introductory science and math courses and would make valuable additions to the STEM workforce. However, students abandon STEM majors at an alarming rate. For example, high performing students frequently cite uninspiring introductory courses as a factor in their choice to switch majors. Low performing students with a high interest and aptitude in STEM careers often have difficulty with the math required in introductory STEM courses with little help provided by their universities. Reshaping how students learn these concepts in elementary, middle and high school will improve student interest and performance in these subjects, thus positively retaining them in STEM majors and helping correct the problem.
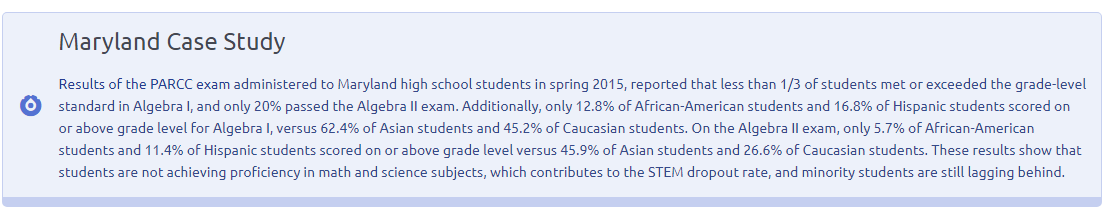
Minority Factors Influence National STEM Divide
Additionally, there is another “divide” that plays a critical role in our country’s existing STEM crisis—a minority divide. According to a 2006 study, 73% of America’s scientists and engineers were white (55% men, 18% women). In 2012, traditionally underrepresented groups—African Americans, Latinos and Native Americans—ages 18 to 24 comprised 34% of the total U.S. population, but only earned 12% of all undergraduate degrees in engineering. Similarly, in 2013, African-Americans and Latinos comprised 28% of the population, but only 7% of the STEM workforce. Yet, minority students expressed desire to have a career in STEM at a rate that was equal to white and Asian students, with research reporting this all the way back into the 1980s. It is a national imperative to boost minority students’ success in STEM subjects.


In2it Learning Bridges the STEM Divide through Intuitive Instruction
According to the U.S. Department of Education FY2014 Budget Request, Cross Cutting Issues: STEM Education, “Despite an annual federal investment of almost $3 billion, too many American students are unprepared in math and science, particularly students from underrepresented groups.” STEM education advocates often indicate the need to reform high school and college course instruction and curriculum to remedy the long-term, chronic shortage of STEM graduates.
For years, students have struggled with connecting the theories of science, technology, engineering and mathematics subjects. In part, this disconnect resulted from the way these subjects have been traditionally taught—conceptually and completely independent of each other, with an emphasis on memorization not comprehension. In response to the STEM divide, In2it Learning developed an interactive teaching model that engages children from ages 5 to 17, with a focus on integrating STEM concepts by solving problems through practical application.
Supporting PCAST Recommendations
In2it Learning’s curriculum model incorporates two PCAST recommendations to achieve the goal of increasing STEM graduates. Specifically, In2it Learning courses replace standard courses with discovery-based research courses so that students are fully engaged in the learning process. Giving young minds the skills to solve problems intuitively helps them mentally connect computer science, math, physics and engineering concepts and teaches them how to use these skills within creative design and artistic applications. As a result, students exhibit greater enthusiasm and confidence in math and related subjects.
Additionally, In2it Learning’s method focuses on logic, analysis and, problem-solving—characteristics that are highly desired by employers. In2it Learning goes beyond just the technical skills of advanced science, math, engineering, physics and programming to give students confidence in critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Given the emphasis on problem-solving that companies are expecting, the learning method taught by In2it Learning will help prepare the future STEM workforce to meet the evolving demands of the workplace environment.
In2it Learning also seeks out strategic alliances with colleges and universities, schools and community organizations, which support PCAST’s recommendation to encourage partnerships among stakeholders to diversify pathways to STEM careers. Currently, In2it Learning affiliates with Mason Game & Technology Academy (MGTA) to offer classes at George Mason University. To learn more about In2it Learning’s partnerships, click here .
Part of the Solution—In2it Learning
In2it Learning recognizes its opportunity to be an integral part of the solution by bridging the STEM workforce gap and enhancing students’ ability to think critically and solve complex problems. By designing classes for young learners that combine STEM subjects in an intuitive way, we believe that all children—regardless of their socio-economic status—can learn accelerated math, science and engineering concepts and use them to solve complex problems while sparking their creativity, reinforcing their abilities and boosting confidence. Our inclusive instruction accounts for student differences in learning styles and builds strong logic and problem-solving skills that are critically needed no matter what career path is chosen.
In2it Learning empowers the next generation of students to successful navigate STEM subjects—in high school, college and beyond—making them more competitive in an international marketplace.
For more information and to learn about classes, contact info@in2it-learning.com.
